From NPR, National Public Radio, Illinois, FM 91.9 UIS
First Came Kidney Failure. Then There Was The $540,842 Bill For Dialysis
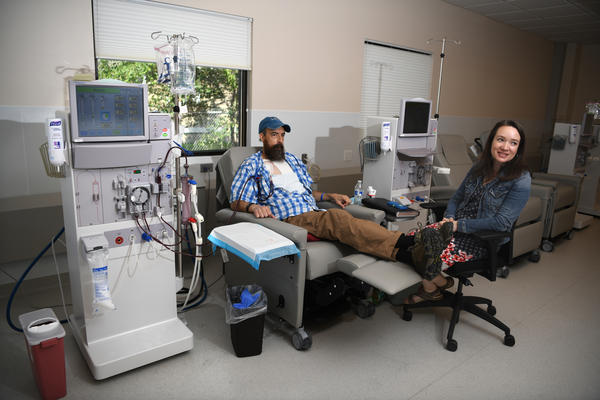
Sovereign Valentine and his wife, Jessica, wait as a dialysis machine filters his blood. Before finding a dialysis clinic in their insurance network, the Valentines were charged more than a half-million dollars for 14 weeks of treatment.
TOMMY MARTINO/KAISER HEALTH NEWS
Several days after NPR published and aired the following story, Fresenius Medical Care, one of the two largest dialysis providers in the U.S., agreed to waive its $524,600.17 charge.
For months, Sovereign Valentine had been feeling progressively run-down. The 50-year-old personal trainer, who goes by "Sov," tried changing his workout and diet to no avail.
Finally, one Sunday, he drove himself to the hospital in the small town of Plains, Mont., where his wife, Jessica, happened to be the physician on call. "I couldn't stop throwing up. I was just toxic."
It turned out he was in kidney failure and needed dialysis immediately.
"I was in shock, but I was so weak that I couldn't even worry," he said. "I just turned it over to God."
He was admitted to a nearby hospital that was equipped to stabilize his condition and to get his first dialysis session. A social worker there arranged for him to follow up with outpatient dialysis, three times a week. She told them Sov had two options, both about 70 miles from his home. They chose a Fresenius Kidney Care clinic in Missoula.
A few days after the treatments began, an insurance case manager called the Valentines warning them that since Fresenius was out of network, they could be required to pay whatever the insurer didn't cover. The manager added that there were no in-network dialysis clinics in Montana, according to Jessica's handwritten notes from the conversation. (The insurance company disputes this and says that its case manager told her there were no in-network dialysis clinics in Missoula.)
Jessica repeatedly asked both the dialysis clinic staff and the insurer how much they could expect to be charged, but couldn't get an answer.
Then the bills came.
Patient: Sovereign Valentine, 50, a personal trainer in Plains, Mont. He is insured by Allegiance through his wife's work as a doctor in a rural hospital.
Total bill: $540,841.90 for 14 weeks of dialysis care at an out-of-network Fresenius clinic. Valentine's insurer paid $16,241.73. The clinic billed Valentine for the unpaid balance of $524,600.17.
Service provider: Fresenius Medical Care, one of two companies (along with rival DaVita) that control about 70% of the U.S. dialysis market.
Medical treatment: Hemodialysis at an outpatient Fresenius clinic, three days a week for 14 weeks.
What gives: As the dominant providers of dialysis care in the U.S., Fresenius and DaVita together form what health economists call a "duopoly." They can demand extraordinary prices for the lifesaving treatment they dispense — especially when they are not in a patient's network. A 1973 law allows all patients with end-stage renal disease like Sov to join Medicare, even if they're younger than 65 — but only after a 90-day waiting period. During that time, patients are extremely vulnerable, medically and financially.
Fresenius billed the Valentines $524,600.17 — an amount that is more than the typical cost of a kidney transplant. It's also nearly twice Jessica's medical school debt. Fresenius charged the Valentines $13,867.74 per dialysis session, or about 59 times the $235 Medicare pays for a dialysis session.
When Jessica opened the first bill, she cried. "It was far worse than what I had imagined would be the worst-case scenario," she said.
Sov had a different reaction: "To me, it's so outrageous that I just have to laugh."
Dialysis centers justify high charges to commercially insured patients because they say they make little or no money on the rates paid for their Medicare patients, who — under the 1973 rule — make up the bulk of their clientele. But nearly $14,000 per session is extraordinary. Commercial payers usually pay about four times the Medicare rate, according to a recent study.
Dialysis companies are quite profitable. Fresenius reported more than $2 billion in profits in 2018, with the vast majority of its revenue coming from North America.
The discrepancy in payments between Medicare and commercial payers gives dialysis centers an incentive to treat as many privately insured patients as possible and to charge as much as they can before dialysis patients enroll in Medicare. It may also give dialysis centers an incentive to charge outlandish prices to the few out-of-network patients they see.
"The dialysis companies may think they can get closer to what they want from the health plans by staying out of network and charging these prices that are totally untethered to their actual costs," said Sabrina Corlette, a professor at Georgetown University's Health Policy Institute. "They have the health plans over a barrel."
One potential way to save costs on dialysis is to switch to a type that can be done at home, which involves infusing fluid into the abdomen. Called peritoneal dialysis, it is common in Europe but relatively rare in the U.S. In an executive order this month, President Trump announced new incentives to increase uptake of those options.
Brad Puffer, a spokesman for Fresenius Medical Care North America, said the company would not comment on any specific patient's situation.
"This is one example of the challenges that can arise from a complex healthcare system in which insurers are increasingly shifting the financial burden to patients," Puffer said in a written statement. "The insurance company should accurately advise patients of in- and out-of-network providers. It is the patient's choice when they receive that information as to which provider they select."
Resolution: As a physician, Jessica Valentine is savvy about navigating the insurance system. She knew it was important to find an in-network provider of dialysis. She and the insurance company case manager both searched on the insurer's online provider directory, she said, and were unable to find one. The problem may have been searching for a "provider" rather than a "facility" in the directory.
Jessica eventually wrote to the Montana insurance commissioner to inquire if the lack of a dialysis provider violated a requirement that insurers maintain an "adequate network" of providers.
With help from the state insurance commissioner, she learned that there was, in fact, an in-network dialysis clinic run by a nonprofit organization that had not turned up in her insurer's online search or the directory. She immediately arranged for Sov to start getting further dialysis there. But the bills with Fresenius, meanwhile, were adding up.
After a reporter made inquiries, a financial counselor at Fresenius told Jessica that the Valentines qualified for a discount of 50%, based on their income. That would still leave them a bill of $262,400.08.
"It's still a completely outrageous charge," Jessica said. "I want to pay what we owe and what's reasonable and what his care actually cost."
Unwilling to pay Fresenius more, Allegiance said Jessica should have found the in-network facility earlier. "There is always the potential for customers to misunderstand information about how their health plan works, especially in stressful situations," a spokesperson for Allegiance wrote.
Jessica is considering contacting a lawyer. If all else fails, the Valentines will consider filing for bankruptcy. A family doctor who works at a rural hospital, Jessica now understands why some of her patients avoid testing and treatment for fear of the cost. "It's very, very frustrating to be a patient, and it's very disempowering to feel like you can't make an informed choice because you can't get the information you need."
The takeaway: Dialysis is a necessary, lifesaving treatment. It is not optional — no matter a patient's financial situation.
Insurers are obligated to have adequate networks for all covered medical services in their plans, though "adequacy" is poorly defined.
So, if it looks like there isn't an in-network option within a reasonable distance — for dialysis or more basic services from orthopedists or dermatologists — keep digging. Keep in mind that dialysis clinics may be listed as "facilities" rather than "providers" in your directory.
If none are available, seek help from your state's insurance commissioner. Report your experiences — that's one way the commissioner can learn that the names listed in the directory aren't taking patients or are 50 miles away, for example.
If you have insurance through an employer, you can contact your benefits department to go to bat for you. If there is no in-network option, you should get a dispensation to go out of network at in-network rates and with in-network copayments.
If you receive a bill for out-of-network care, don't merely write the check. Ask for an itemized bill and review the charges. You can also ask your insurance company to negotiate with the provider on your behalf. See if the bill counts as a "surprise bill" under your state's law, in which case you could be "held harmless" from excessive charges.
And when all else fails, try to negotiate directly with the provider. They might have a financial assistance policy, or be willing to lower the cost significantly to avoid turning you over to a debt collector that would pay them pennies on the dollar.
NPR produced and edited the interview with Kaiser Health News' Elisabeth Rosenthal for broadcast. Nick Mott of Montana Public Radio provided audio reporting. The digital version of this story was updated July 22 to include a fuller explanation of the insurance company's account of what the Valentines were told about dialysis clinics in its network.
Bill of the Month is a crowdsourced investigation by Kaiser Health News and NPR that dissects and explains medical bills. Do you have an interesting medical bill you want to share with us? Tell us about it here.
Dialysis Hydration Monitoring
From AZO Sensors
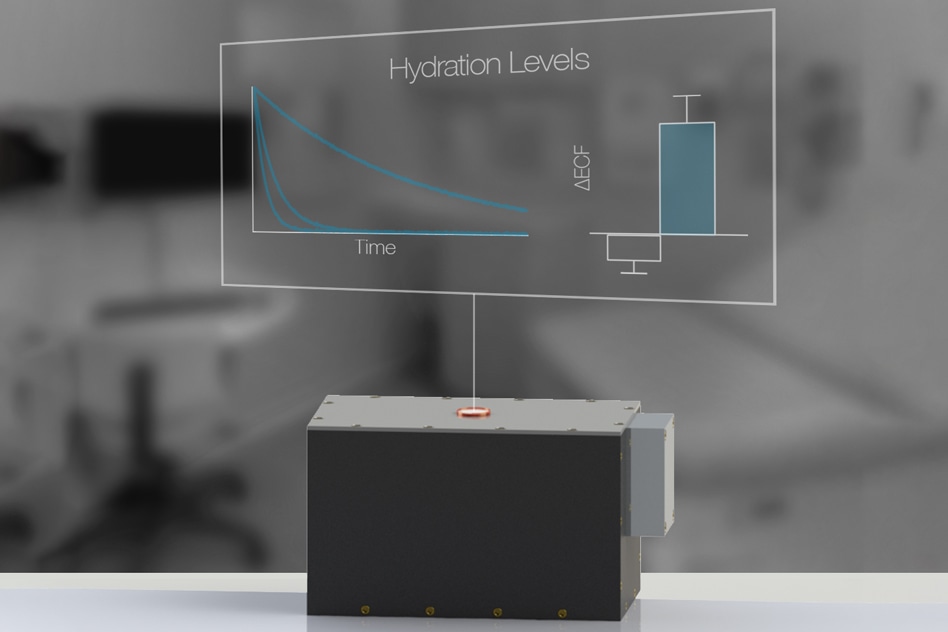
This usually involves guess-work on how much water needs to be removed, and the patient also needs to be carefully monitored for sudden drop in blood pressure.
A present, no easy and reliable method is available to determine hydration levels in such patients, who number about half a million in the U.S. Conversely, a research team from Massachusetts General Hospital and MIT has designed a new, portable sensor that can precisely determine the hydration levels of patients using a method called nuclear magnetic resonance, or NMR, relaxometry.
A device like that would be useful for dialysis patients and also for people suffering from congestive heart failure. The device can also benefit athletes and elderly population who may be at risk of becoming dehydrated, stated Michael Cima, the David H. Koch Professor of Engineering in MIT’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
There’s a tremendous need across many different patient populations to know whether they have too much water or too little water. This is a way we could measure directly, in every patient, how close they are to a normal hydration state.
Michael Cima, Study Senior Author and Member of Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, MIT
While the new device is predicated on the same technology as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scanners, it can achieve measurements in relatively less time and at a fraction of the cost of MRI. This is because imaging is not involved in this process.
The lead author of the paper is Lina Colucci, a former graduate student in health sciences and technology. The study has been reported in in the July 24th, 2019 issue of Science Translational Medicine.
Other study authors include MIT graduate student Matthew Li; MGH nephrologists Andrew Allegretti, Kristin Corapi, and Herbert Lin; MGH research fellow Xavier Vela Parada; Harvard Medical School assistant professor in radiology Matthew Rosen; and MGH Chief of Medicine Dennis Ausiello.
Hydration Status
Cima started working on this study around a decade ago, after he came to know that there was an urgent need for a noninvasive ad precise method to determine hydration levels. At present, the existing techniques are subjective, invasive, or inconsistent. Most often, physicians assess overload (hypervolemia) by several physical signs like assessing the jugular vein size, examining the ankles where water may collect, or pressing on the skin.
The MIT researchers decided to go for an entirely different technique, predicated on NMR. Earlier, Cima had established a company, known as T2 Biosystems, that utilizes tiny NMR devices to diagnose bacterial infections by examining blood samples of patients.
Cima later devised an idea to apply the devices to determine water content in tissue, and several years ago, the team received a grant from the MIT-MGH Strategic Partnership to conduct a minor clinical trial for tracking hydration. The researchers examined patients with end-stage renal disease who frequently underwent dialysis and also healthy controls.
One major objective of dialysis is to remove fluid from patients and bring them to their “dry weight”. Dry weight is the weight at which the fluid levels of patients are improved. However, it is very difficult to determine a patient’s dry weight. As such, dry weight is estimated by physicians based on physical signs and also via trial-and-error over many dialysis sessions.
The MIT/MGH research team demonstrated that quantitative NMR, which operates by determining a trait of hydrogen atoms known as T2 relaxation time, can enable relatively more precise measurements. The T2 signal determines the environment as well as the amount of hydrogen atoms, or water molecules, present.
The beauty of magnetic resonance compared to other modalities for assessing hydration is that the magnetic resonance signal comes exclusively from hydrogen atoms. And most of the hydrogen atoms in the human body are found in water molecules.
Lina Colucci, Study Lead Author and Former Graduate Student, Health Sciences and Technology, MIT
The investigators applied their new device to determine the level of fluid in patients both before and after they went through dialysis. The outcomes demonstrated that this method can possibly differentiate healthy patients from those requiring dialysis with just the initial measurement. Moreover, the measurement precisely demonstrated dialysis patients reaching closer to a usual hydration state over the duration of their therapy.
Additionally, the NMR measurements successfully detected the presence of surplus fluid within the body before conventional clinical signs—for example, the accumulation of visible fluid under the skin—were present. Doctors can use the sensor to establish when a patient has approached his or her actual dry weight, and this determination can be personalized during every dialysis treatment.
Better Monitoring
The scientists are now planning to conduct more clinical trials with dialysis patients. They believe that dialysis, which presently costs the U.S. over $40 billion per annum, would be one among the largest applications for this kind of technology. Such a monitoring can also prove useful for patients suffering from congestive heart failure, which impacts around 5 million people in the U.S, alone.
The water retention issues of congestive heart failure patients are very significant. Our sensor may offer the possibility of a direct measure of how close they are to a normal fluid state. This is important because identifying fluid accumulation early has been shown to reduce hospitalization, but right now there are no ways to quantify low-level fluid accumulation in the body. Our technology could potentially be used at home as a way for the care team to get that early warning.
Michael Cima, Study Senior Author and Member of Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, MIT
According to Sahir Kalim, a nephrologist and assistant professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, the MIT approach is “highly novel.”
“The development of a bedside device that can accurately inform providers about how much fluid a patient should ideally have removed during their dialysis treatment would likely be one of the most significant developments in dialysis care in many years,” stated Kalim, who was not part of the research. “Colucci and colleagues have made a promising innovation that may one day yield this impact.”
In their analysis of the healthy control subjects, the investigators also observed that dehydration can possibly be detected. This would render the device handy for tracking elderly population, who usually become dehydrated since their sense of thirst reduces with age, or athletes participating in endurance events, including marathons. The team is now planning some upcoming clinical trials so as to test the capability of the novel technology to identify dehydration.
The study was funded by the MGH-MIT Strategic Partnership Grand Challenge, the Air Force Medical Services/Institute of Soldier Nanotechnologies, the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowships Program, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, the Koch Institute Support (core) Grant from the National Cancer Institute, and Harvard University.

